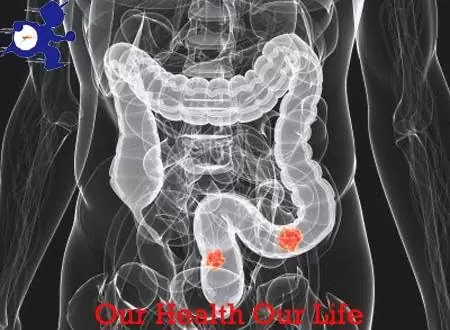
The colon or large intestine is down the gastrointestinal tract. Its main function is to reduce the volume of stool (by absorbing water) and store them for later remove them at the right time. Today, we discuss about what is colon cancer and how to prevent colon cancer.
Colorectal cancer or colon cancer.
Currently, colon cancer or colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death, after breast cancer in women and lung cancer in man. The healing of colon cancer depends primarily on the stage at which it is diagnosed: if caught in the early stages a complete cure is achieved in most cases; when diagnosed in advanced stages only a small percentage of patients survive five years. With preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing colon cancer. Therefore it is desirable to know the risk factors, symptoms and methods can help diagnose this cancer in stages where it is curable, even prevent its onset.
Colon cancer develops from noncancerous lesions, called adenomatous polyps. A polyp is a protrusion in the colonic mucosa, which could compare with skin warts. Grows slowly over the years. Most people have no polyps before 50 years of age. Some polyps can develop into cancer (after growth over several years) and others not. One way to prevent colon cancer is whether these polyps exist and, if so, remove them before they become malignant. It has been shown that removal of these polyps prevents colon cancer.
[ads]
How Is my risk of colon cancer?
Each person has an individual risk of colon cancer. This risk depends on many factors and some of them are clearly established.
- A person has a “standard” risk of colon cancer if you have more than 50 years and has none of the risk factors set forth below.
- A person has an increased risk compared to the general population of developing colon cancer if:
- have a personal history of colon cancer or adenomatous polyps.
- have a family history (parents, siblings and / or children) with colon cancer or adenomatous polyps.
- have a family history of multiple cancers, especially breast, ovary and uterus.
- If you have been diagnosed with chronic inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease).
There are also some hereditary diseases that pose a very increased risk of developing colon cancer risk, but are rare.
Other factors that may pose a higher risk include:
- Low fiber diet rich in fats.
- Sedentary life.
What are your symptoms?
In general, colon cancer at its beginning does not have to cause any symptoms. However, in its evolution, it can cause:
- Rectal Bleeding is manifested by red blood (though it may be dark) with deposition.
- Changes in bowel habits, mainly sudden constipation, or acintadas stools.
- Lower abdominal pain.
- Abdominal distension.
- Abdominal discomfort urgently deposition or feeling the need to defecate without subsequent deposition.
- Weight loss is not justified by decreased intake.
- Weariness anemia secondary to bleeding.
The occurrence of any of these symptoms should be considered a reason for medical consultation. It is important to note that are not specific and may occur without any significant disease is found, but the significance of these symptoms you should set the doctor.
Is it advisable to follow a preventive program?
The reasons which led to medical societies to raise the option of a preventive program are:
- The possibility of diagnosing cancer when in initial stages and, therefore, curable (often in these cases no symptoms).
- The ability to detect and remove (adenomatous polyps) pre-cancerous lesions, thus preventing its evolution to malignancy.
What kind of preventive or early diagnostic exist today?
There are several alternatives. The choice between them depends on the decision of each person adequate information from your doctor. In principle, as a rule, it is advisable to start any of these measures in the general population from age 50, or earlier if there are risk factors.
- DRE: is part of the general physical examination.
- Test Fecal Occult Blood: to detect small amounts of blood in the stool, which are not identifiable at a glance. It can be done at home and send the samples to a medical center. It is important to follow the instructions to be effective, since the result may not be accurate due to multiple causes. Furthermore, to achieve good results in terms of prevention, it is necessary to perform this test at least biannual frequency. If the test is positive, further exploration is needed to detect the cause of bleeding.
- Sigmoidoscopy: is the introduction of a flexible through the anus, which has a video system at its end tube and can see in this way the intestinal wall in a particular length (the left portion of the colon). They can detect and treat polyps or cancer of colon explored. This test requires preparation to cleanse the colon, and allow better visualization of the wall. Abdominal discomfort produced by air introduced through the tube, which in general are not very important and need no sedation. The existence of injury may necessitate a complete scan of the colon.
- Colonoscopy: a flexible, similar to the previous, but longer tube is used, and the entire colon wall is. Requires greater preparation (cleaning) of the colon, and produce more discomfort than sigmoidoscopy, so various types of sedation frequently used. To view the entire colon can detect and treat injuries by any stretch of it.
- Barium enema: a substance through the anus which is visible on X-ray the colon is filled in this way and radiographs are taken is introduced. It could be compared with the negative of a photograph. There are several techniques to improve resolution. Allows only detect lesions but is not possible to sample them or remove them, so that in case of finding any alteration, need for additional scans. Requires similar to colonoscopy and produces some abdominal discomfort by the contrast material and introduced air preparation, although they are generally more mild discomfort that caused by colonoscopy.
- Other explorations: currently being developed techniques aimed see the colon wall in full, decreasing the discomfort associated with colonoscopy. This is the case of so-called “virtual colonoscopy”, which is a radiology technique that allows the inside of the colon without inserting a tube through the anus. However, although a promising and already highly developed technique useful in this field is not yet fully consolidated.
- Also under investigation in the efficacy of certain blood or feces, although in this case we still have only preliminary results and not applicable to routine clinical practice.
Are there habits to reduce the risk of colon cancer?
There is no way to completely eliminate the risk of developing colon cancer, hence the usefulness of preventive programs arises. However, some tips that appear to be useful in reducing this risk are:
- Follow a diet rich in fiber: fruits, vegetables, grains.
- Avoid foods based diets high in fat, especially saturated fat.
- Taking calcium-rich foods.
- Physical exercise regularly.
We are researching the usefulness of some drugs in the prevention of colon cancer, although there are still no definitive results.








Modern era age all of should a knowledge colon cancer…………………….now a days it’s harming our health………..all of visit this site and know it’s easily